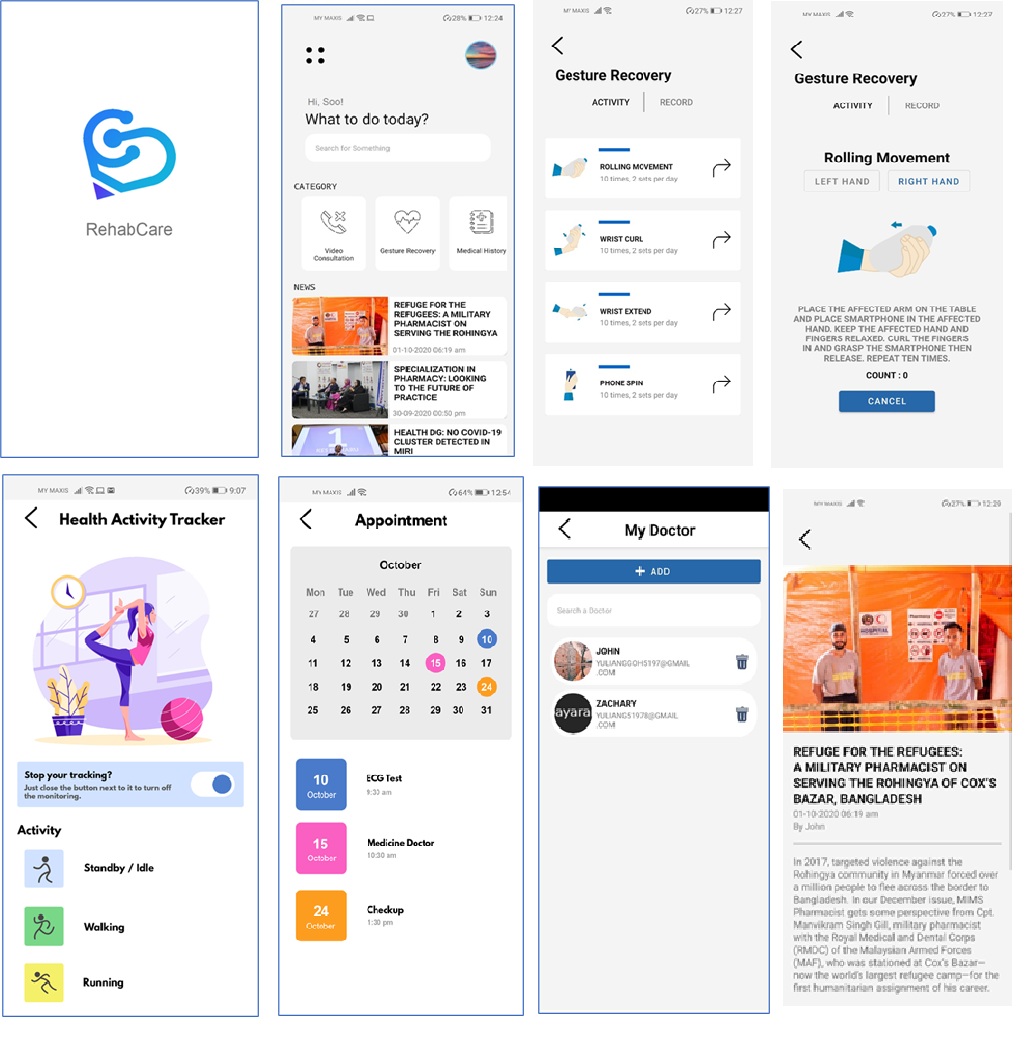
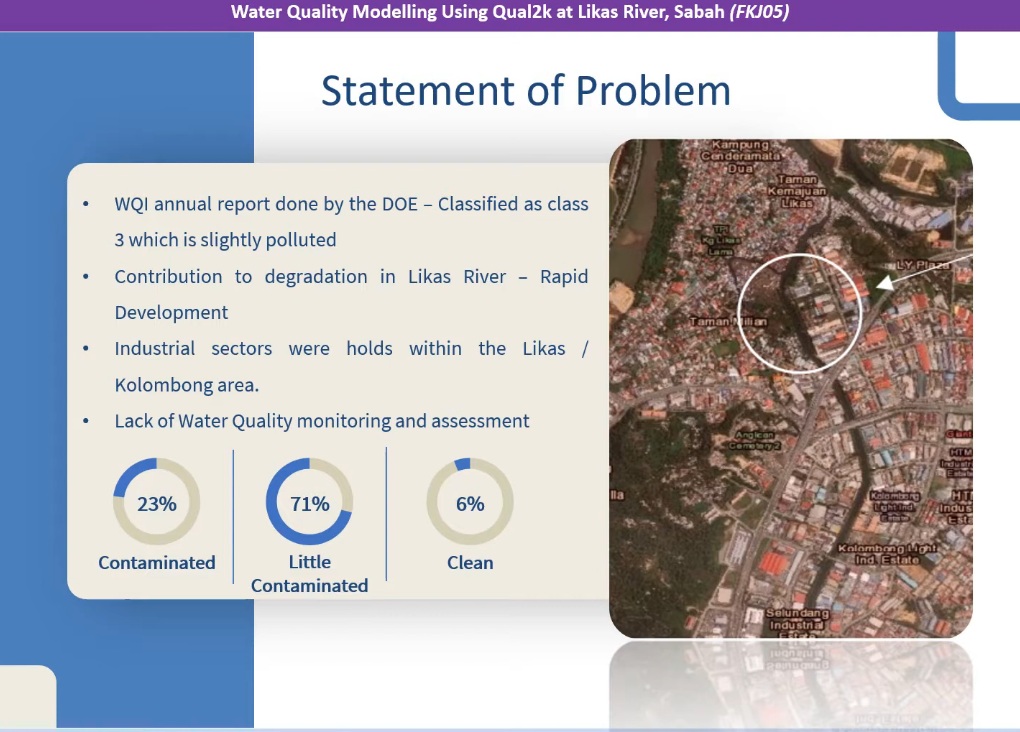
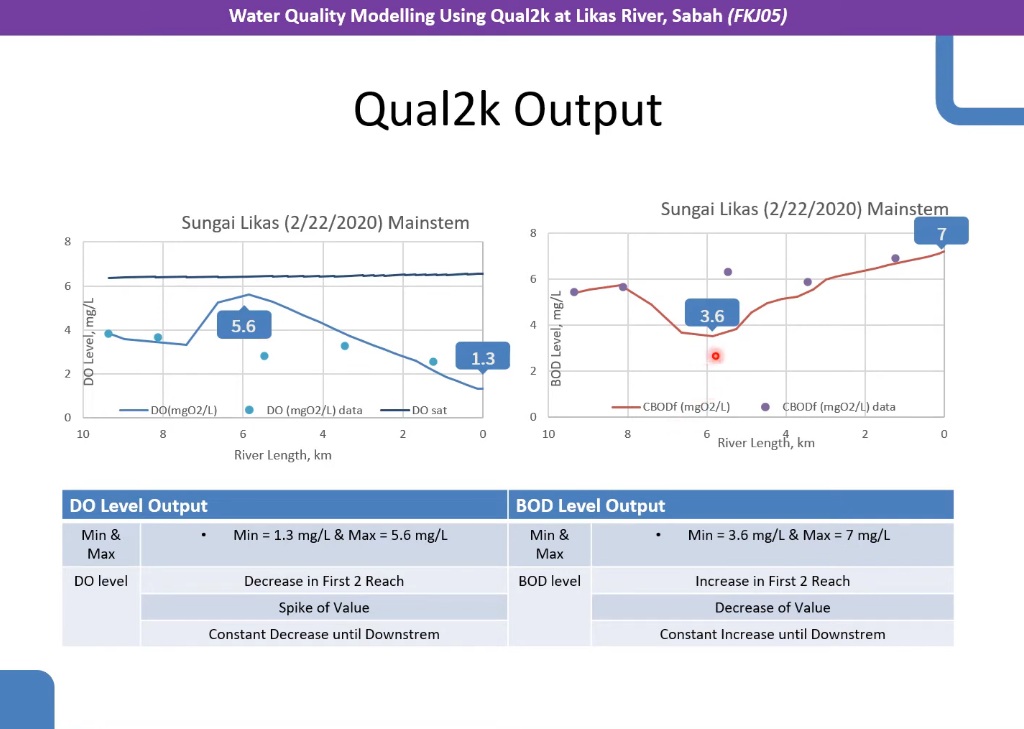
SDG 1–3: Social Well-Being, Poverty Alleviation & Healthy Communities
Student innovations that uplift lives and strengthen community resilience
UMS students frequently develop impactful research that addresses poverty reduction, food security, healthcare access, mental health, and community empowerment. Projects include rural poverty mapping, nutrition intervention programmes, low-cost health monitoring tools, counselling programmes for youth, community entrepreneurship models, and food bank optimisation systems. Many of these works are implemented in B40 communities, schools, coastal villages, and rural districts throughout Sabah, contributing directly to stronger, healthier, and more resilient societies.
SDG 4–6:Quality Education, Water Security & Environmental Health
Developing accessible education and sustainable resource solutions
Students from education, science, engineering, and computing faculties create projects that strengthen learning accessibility, water conservation, water filtration systems, environmental monitoring, and indigenous curriculum development. These include low-cost water filters for rural areas, AI-driven environmental sensors, STEM learning modules for rural schools, literacy tools for indigenous children, and smart sanitation systems. Such projects enhance both community well-being and environmental sustainability in underserved areas.
SDG 7–9: Renewable Energy, Green Technology & Innovation-Driven Economy
Engineering, computing, and business students creating future-ready technologies
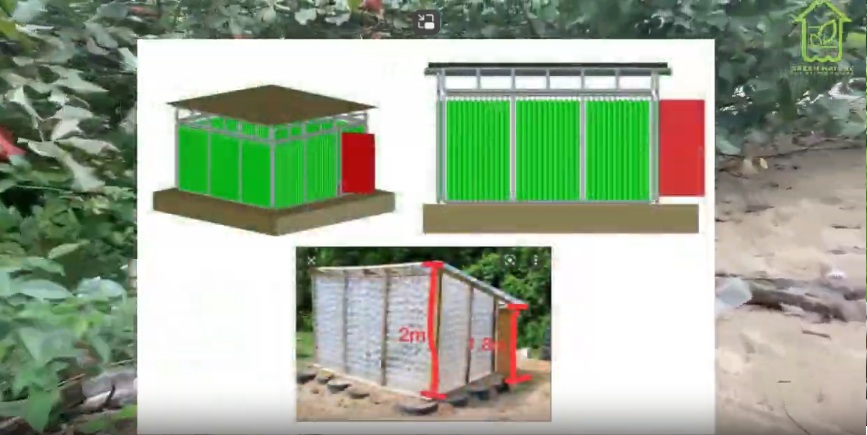
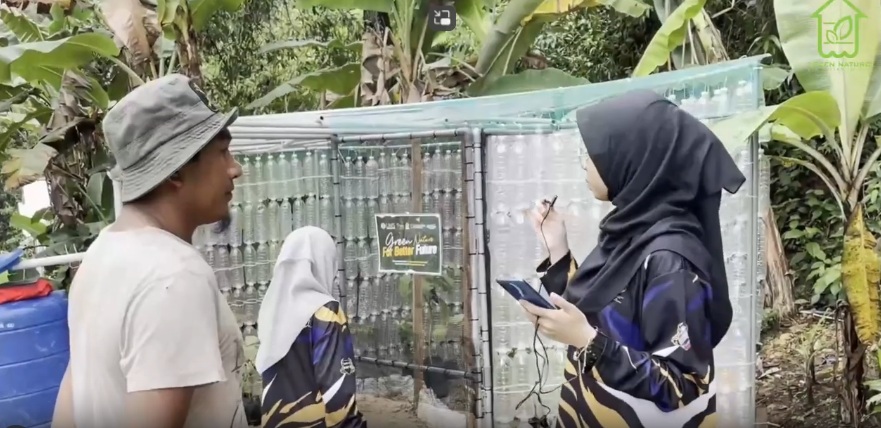
UMS students regularly produce cutting-edge sustainable technologies such as solar-powered devices, micro-hydro energy systems, IoT-based smart farming, energy-efficient building models, green logistics optimisation, sustainable finance assessment tools, and digital applications for carbon tracking. Engineering and computing students work closely with the Solar Energy Management System, ATOM@UMS (nuclear science), smart device labs, and industrial partners to produce prototypes and innovations that enhance regional green technology development.
SDG 10–12: Inclusive Development, Responsible Consumption & Circular Economy
Student-led sustainability solutions for waste reduction and equitable growth
Across business, social sciences, food science, and agricultural disciplines, UMS students innovate in sustainable consumption, behavioural sustainability, waste-to-resource conversion, and ethical production systems. FYPs include biodegradable packaging from local biomass, food waste composting systems, circular agriculture models, social inclusion studies, sustainable tourism frameworks, and micro-enterprise development for rural women. These works support Sabah’s transition toward a circular economy and more inclusive development.
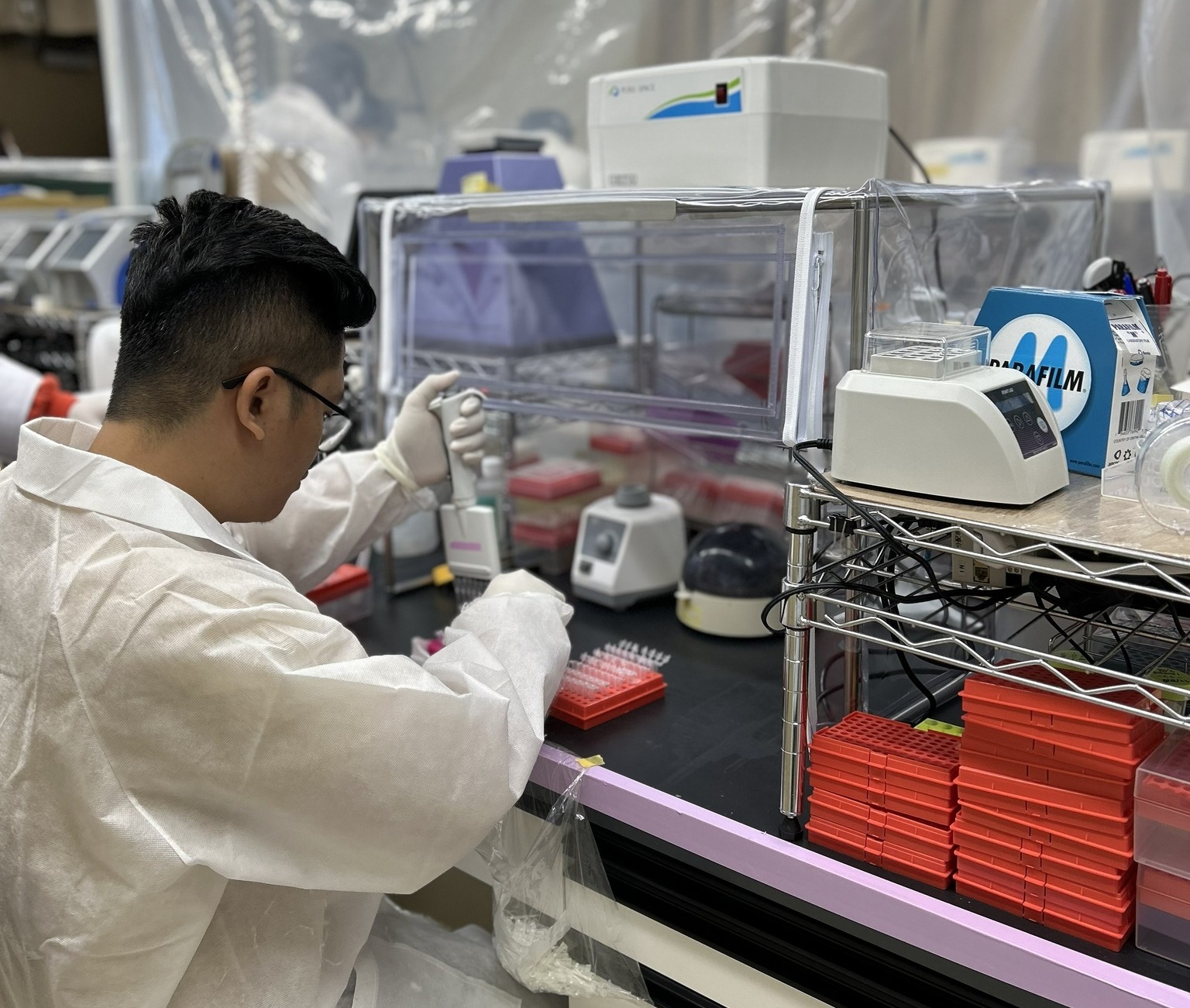
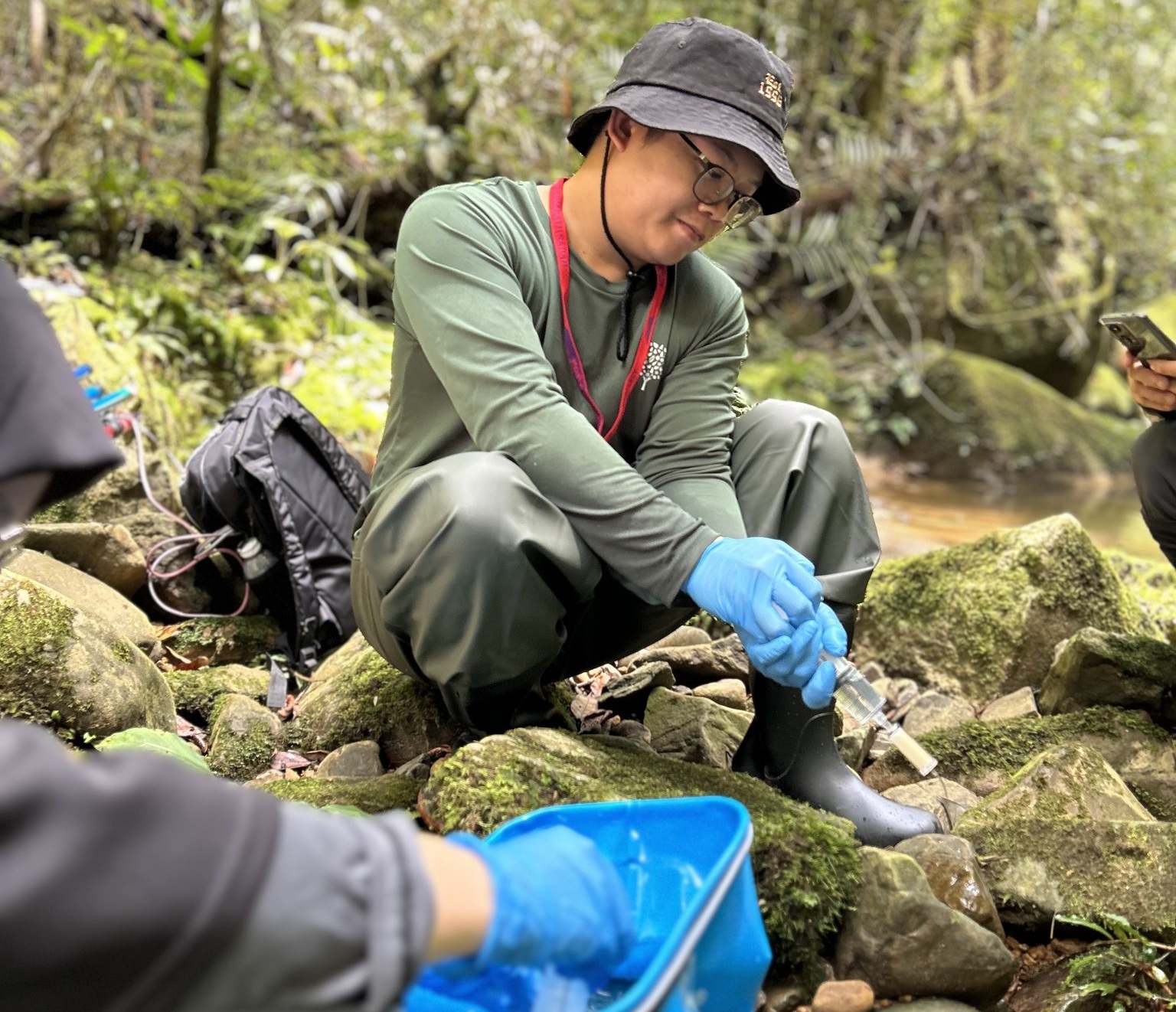
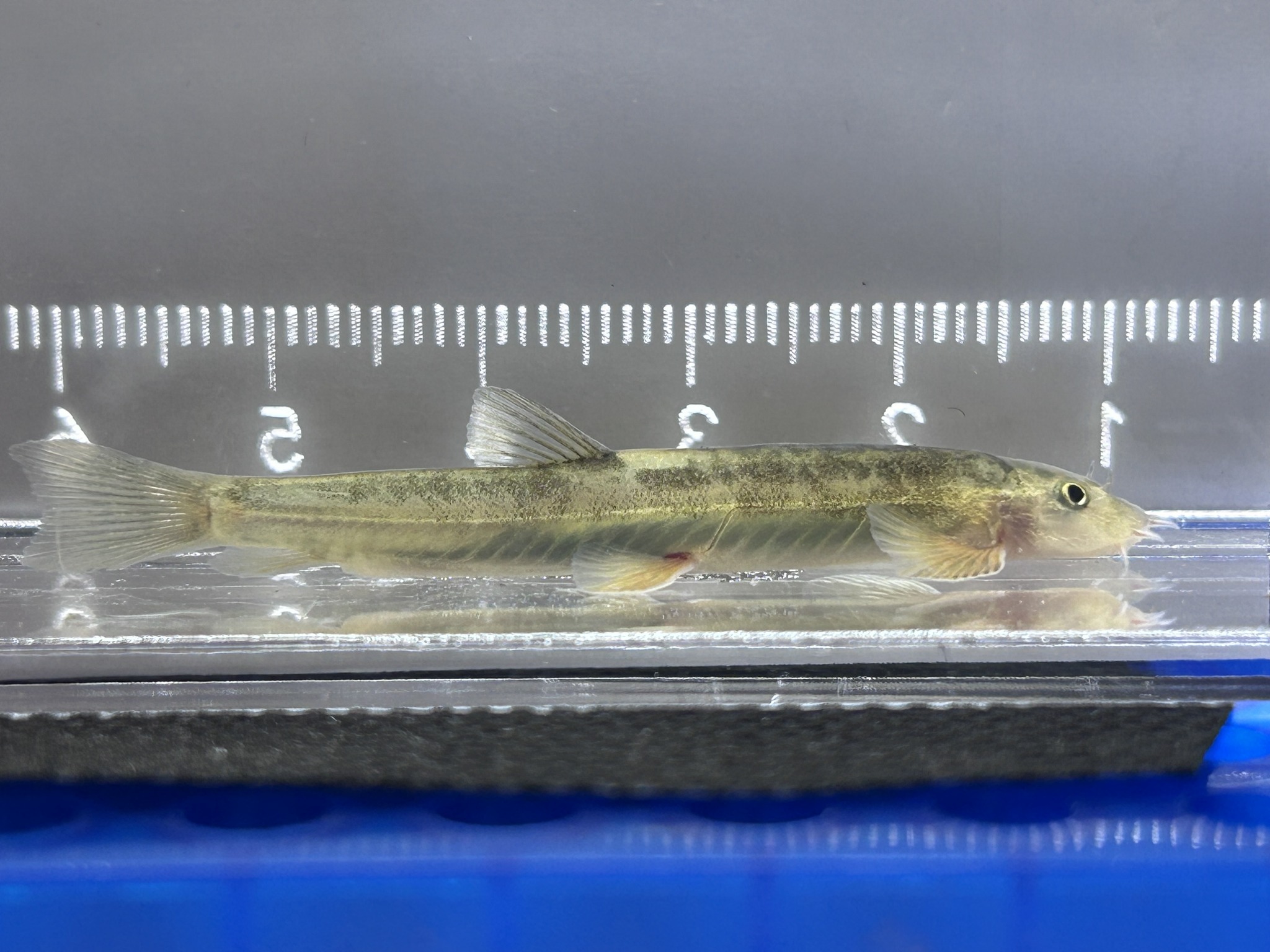
SDG 13–15: Climate Action, Biodiversity Conservation & Ecosystem Resilience
Harnessing Sabah’s ecosystems as outdoor laboratories for conservation-focused projects
With access to one of the world’s most biodiverse environments, UMS students—especially from ITBC, BMRI, FST, and FPTF—produce impactful research on wildlife conservation, coral rehabilitation, reforestation, seagrass ecology, watershed management, mangrove restoration, and climate risk assessment. Students engage directly in fieldwork within UMS living labs, marine parks, forest reserves, and rural landscapes, generating conservation data that supports government agencies, NGOs, and community organisations.
SDG 16–17: Governance, Indigenous Rights & Global Partnerships
Strengthening institutions, cultural heritage, and international collaboration
UMS students from FSSK, BorIIS, Islamic Studies, and the Academy of Arts & Creative Technology conduct FYPs on indigenous rights, cultural documentation, governance models, heritage preservation, peace and conflict studies, and international cooperation. Projects often involve digitising oral histories, preserving endangered languages, analysing governance structures, mapping cultural heritage sites, and partnering with local organisations to strengthen community leadership. These works advance sustainable governance and cultural continuity across Borneo.
UMS: A Campus Where Students Lead Sustainable Change
Together, these student projects reflect UMS’s strong culture of sustainability scholarship, innovation, and community impact. Across all faculties and research institutes, UMS empowers students to address real-world problems, collaborate with local communities, and apply knowledge that contributes directly to sustainable development.
By fostering creativity, scientific inquiry, cultural appreciation, and social responsibility, UMS continues to cultivate a generation of graduates who will shape the future of Sabah and the world—proving that meaningful sustainability solutions can begin with student ideas, research, and passion.



 Empowering UMS Students to Create Real-World Solutions Aligned with the SDGs
Empowering UMS Students to Create Real-World Solutions Aligned with the SDGs